Scholarship Portal Process:
Prequalifying questions
Register Account
Student Dashboard
Application
Question and Answer Sections:
This section includes a short essay section: What are your college/career plans? What inspired you to follow this path?
See Application Tips for list of essay questions.
Required and Optional Documentation:
Have questions about a specific section? See our Scholarship Portal Help Booklet
Confirmation
Resources:
Need more help?
Scholarship Ambassadors
The following organizations are Community Foundation Scholarship Ambassadors. They have been trained on navigating our scholarship portal and are available to help answer questions and guide you through the application process. Click on the organization for contact information.
Questions about scholarships?
Contact Jessica:
jessica@stclairfoundation.org
810-984-4761
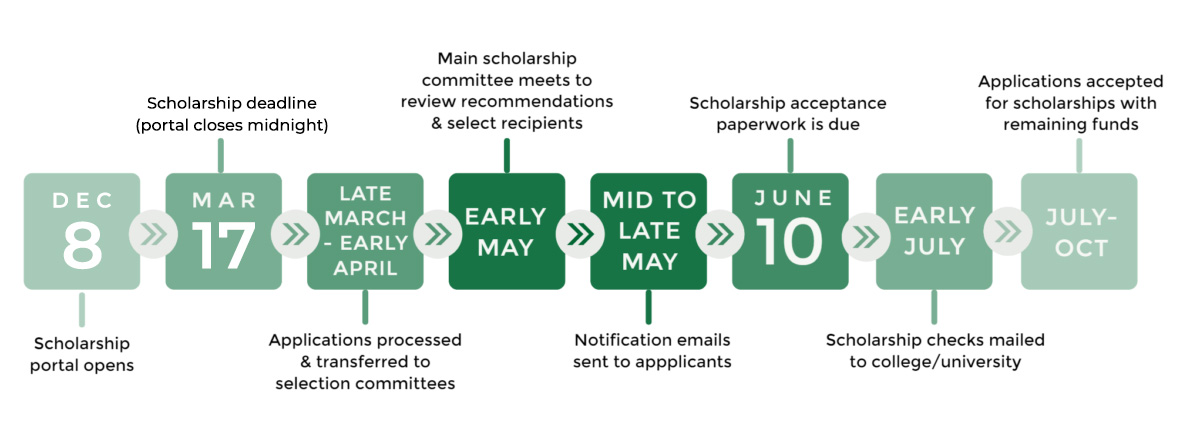
SCHOLARSHIP TIMELINE
Other Scholarship Opportunities
Literacy & Beyond – Scholarship for Mothers
Other Resources
Tuition Incentive Program (TIP)
Frequently Asked Questions
What year did you/do you expect to graduate from high school?
What high school did you/do you expect to graduate from?
Answer the pre-qualifying questions completely and honestly. This will generate a list of scholarship funds for which you are eligible. Checkmark all that appear and create your profile. Returning students should log in to your existing profile.
Once you answer the pre-qualifying questions and start an application you do not need to answer them again. Doing so will only create duplicate applications. Instead, log into your account and resume your application via the Student Dashboard.
College students – An unofficial transcript or internet printout of your transcript is acceptable as long as it is a complete transcript of your college work to date, is clearly labeled with your name, current academic year, your cumulative grade point average, and the name of the college or university.
High school seniors – your complete transcript, including: your first semester senior-year grades, cumulative grade point average, SAT score, and class rank is required.
An older student trying to track down ACT, SAT, Accuplacer or Compass test scores for the required upload may contact the testing center at their college or university, or reach out to the high school from which they graduated as test scores are part of a student’s permanent record.
More recent high school graduates may log into their profile on the SAT or ACT website if the test scores are not already listed on a transcript.
List your score of each section of the GED test. Must students are tested on five sections. This score should be between 200 and 800; your percentile score, which is under 100, indicates how well you did compared to other test-takers but does not directly correspond to a GPA. The score for each of the sections can be used to determine your average GED score, which is the first step in converting it to a GPA.
Divide the Sum of Your Scores by the Number of SectionsAdd together the scores from each section of the GED, then divide this number by the number of sections you took to find your average GED score. For example, if your total score is 3000 and you took five sections, your average GED score would be 600.
Use Your GED Average to Determine Its GPA EquivalentConvert your GED score into an approximate GPA using the following information. A GED score of below 300 is the approximate equivalent of a GPA of 1 or below. A GED score of 300 to 400 is the approximate equivalent of a GPA of 1.5 to 2.0. A GED score of 401 to 500 is the approximate equivalent of a GPA of 2.0 to 2.9. A GED score of 501 to 600 is the approximate equivalent of a GPA of 3.0 to 3.4. A GED score of 601 to 700 is the approximate equivalent of a GPA of 3.5 to 3.7 while a GED score of 701 to 800 is the approximate equivalent of a GPA of 3.8 to 4.0.
